Use Case: Prebid Server | Prebid Mobile SDK
- Workflow
- Details
- Further Reading
Unlike Prebid.js, the Prebid Mobile SDK doesn’t make requests to demand sources directly. Instead, it relies entirely on Prebid Server to handle the bidder communication.
Workflow
Here’s a workflow diagramming how this works.
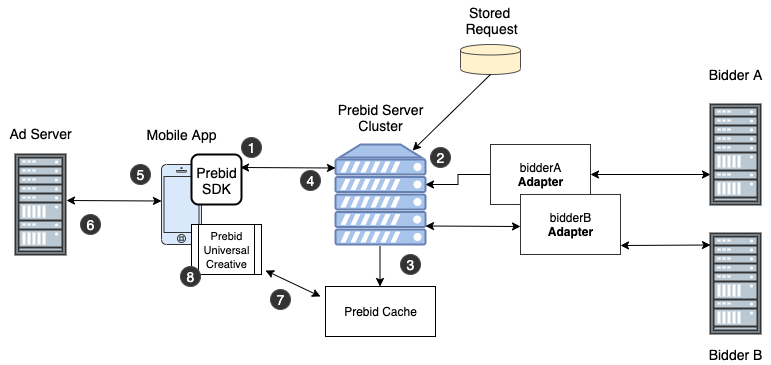
- The mobile app calls Prebid SDK with one or more “stored request IDs”. Prebid SDK forms an OpenRTB request for the auction and calls Prebid Server. This request contains an ad format and one or more “stored request IDs” mapping adunits to bidders and parameters.
- Prebid Server looks up the stored request to find which bidders and parameters to use as well as any privacy regulation enforcement, calling all eligible bidders for bids.
- The auction takes place and bid responses are placed in a cache.
- Prebid Server responds to the Prebid SDK with results and ad server targeting variables.
- The ad server targeting variables are sent along with the ad request to the publisher ad server.
- When header bidding wins in the ad server, the ad server responds with a call to the Prebid Universal Creative.
- The Prebid Universal Creative pulls the winning bid from the Prebid Cache.
- The Prebid Universal Creative displays the winning bid creative from the cache.
Details
The following sections give additional details of the steps provided in the workflows.
Prebid SDK Calls Prebid Server
The iOS and Android SDKs have functions which supply:
- Which Prebid Server host to use
- The account ID for that Prebid Server (obtain this from the Prebid Server host company)
- Ad unit (i.e. ad format) information with a “stored request ID” (obtain these from the host company too)
- First party data
- Privacy information (e.g. a consent string)
The Prebid SDK takes information from these functions and builds out the OpenRTB request, sending it to the named Prebid Server. For example, if the mobile app has this code (in swift for iOS):
// Prebid Server host company or set a custom one
Prebid.shared.prebidServerHost = .custom
// get this ID from your Prebid Server host provider
PrebidMobile.setPrebidServerAccountId("1234");
...
// get PREBID_SERVER_CONFIGURATION_ID from your Prebid Server host provider
BannerAdUnit bannerAdUnit = new BannerAdUnit("PREBID_SERVER_CONFIGURATION_ID", 300, 250);
The resulting OpenRTB generated by the SDK and sent to Prebid Server would be:
{
"id": "random-uuid",
"app": {
"bundle": "AppNexus.PrebidMobileDemo",
"ext": {
"prebid": {
"version": "0.2.0",
"source": "prebid-mobile"
}
},
"publisher": {
"id": "1234" // from PrebidMobile.setPrebidServerAccountId("1234");
},
"ver": "1.0"
},
"imp": [
{
"id": "random-uuid",
"banner": {
"format": [
{
"h": 250,
"w": 300
}
]
},
"ext": {
"prebid": {
"storedrequest": { // this pulls in the bidders and params for the first ad slot
"id": "PREBID_SERVER_CONFIGURATION_ID"
}
}
}
}
],
"ext": {
"prebid": {
"storedrequest": { // this maps to the "top-level" stored request
"id": "1234" // from setPrebidServerAccountId(). Pulls in global behavior (cache, targeting)
}
}
}
}
Of course if there are multiple adunits on your app’s page, there can
be multiple calls to BannerAdUnit() which would generate multiple imp objects in the OpenRTB request.
Prebid Server Receives the Request
The request that comes in from the SDK is more like a skeleton request. There are a number of key components missing, such as which bidders should be called.
Prebid Server Resolves the Stored Request IDs
The example above lists two stored request IDs: the “top-level” ID (1234) and one “adunit-level” ID (PREBID_SERVER_CONFIGURATION_ID).
When Prebid Server sees a stored request ID, it queries a database to pull in the actual contents to be included in the auction.
To continue the example, stored request ID 1234 defines the overall request currency, caching instructions, a custom price granularity, and instructions to include ad server targeting keys for all bidders:
{
"cur": [
"EUR"
],
"ext": {
"prebid": {
"cache": {
"bids": {}
},
"targeting": {
"includewinners": true,
"includebidderkeys": true,
"mediatypepricegranularity": {
"banner": {
"ranges": [
{
"max": 5,
"min": 0,
"increment": 0.01
},
{
"max": 8,
"min": 5,
"increment": 0.1
},
{
"max": 30,
"min": 8,
"increment": 1
}
],
"precision": 2
}
}
}
}
}
}
The PREBID_SERVER_CONFIGURATION_ID would have the list of bidders and params relevant for that ad unit:
{
"ext": {
"bidderA": {
"placementId": "1111"
},
"bidderB": {
"key1": "val1"
}
}
}
The power of this approach is that a number of important header bidding parameters can change without having to change application code!
Auction and Response
From here on out, the header bidding auction is the same as it is for Prebid.js:
- Enforce privacy regulations
- Call the bidders
- Collect responses
- Prepare the OpenRTB response
Prebid Server will cache each bidder’s markup and metadata in Prebid Server’s cache for retrieval at render time.
The SDK Gets the Response
The response from Prebid Server is OpenRTB with some extensions like the ad server targeting. For example, it might look like:
{
"seatbid": [{
"seat": "bidderA",
"bid": [{
...
"ext": {
"prebid": {
"targeting": {
// standard Prebid ad server targeting key/values
"hb_env": "mobile-app",
"hb_pb": "1.20",
"hb_size": "300x50",
"hb_bidder": "bidderA",
// the body of the creative will be retrieved from cache
// if it wins
"hb_cache_id": "20d2e558-67b0-4a43-99ba-f23e3383932e",
"hb_cache_host": "prebid-server.example.com",
"hb_cache_path": "/cache",
...
}
}
}
}]
}]
}
Prebid Server will responde back to Prebid SDK with either all bidder keys, no bidder keys, winning bid or no winning bid depending on the ext.prebid.targeting.includewinners and ext.prebid.targeting.includebidderkeys attributes resolved for the top level stored request of that particular request. Example below:
"ext": {
"prebid": {
"cache": {
"bids": {}
},
"targeting": {
"includewinners": true,
"includebidderkeys": true,
"mediatypepricegranularity": {
"banner": {
...
}
}
}
}
}
The behavior of the keys is:
includewinners: If set to true, Prebid Server will emit the top winning bid ashb_pbformat. If set to false, Prebid Server will not supply the top bid.includebidderkeys: If set to true, Prebid Server will emit all bidder keys ashb_pb_BIDDERNAMEalong with all other bidder specific keys. If false, Prebid Server will not supply any bidder specific keys.
The SDK Receives Prebid Server’s Response
Prebid SDK will set the publisher ad server targeting with all keys received from Prebid Server’s response, unadultered, contained in the ext.prebid.targeting object.
Application Code Calls the Ad Server
The application code is responsible for calling the ad server, with the Prebid keys contained in the request builder object of the ad server set by Prebid Server.
Prebid Wins in Ad Server
When a Prebid ad wins in the ad server, the ad server will return a JavaScript creative to the app’s webview. The ad server response contains within its payload a fetch to the Prebid Univeral Creative.
Prebid Universal Creative Fetches Markup
Prebid Universal Creative loads in the webiview, which sees the hb_env=mobile-app key value pair and realizes its time to load the creative body from the cache parameters: hb_cache_id, hb_cache_host, and hb_cache_path. (Or hb_cache_id_bidderA, hb_cache_host_bidderA, and hb_cache_path_bidderA when in send-all-bids mode.). A fetch is performed to receive the cached object from Prebid Server.
Load Ad
The Prebid Universal Crative will parse the response, looking for the adm object, loading the full markup into the webview.